Housing productivity has emerged as a crucial focus in the ongoing discussion about America’s escalating housing crisis. With the cost of new homes significantly outpacing wage growth, understanding the factors behind this decline in productivity is imperative for fostering housing affordability. Land-use regulation and NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies have long been identified as barriers that stifle the construction industry, leading to a decrease in innovative building practices. This stagnation not only hampers economic growth but also restricts the available housing supply, exacerbating the divide between income levels and home ownership. As we explore how housing productivity has evolved, it becomes clear that addressing these regulatory challenges is vital for revitalizing the housing market.
The efficiency of housing production is increasingly recognized as a vital element in tackling the pressing issue of housing shortages. The juxtaposition of increasing expenses with limited housing options highlights the urgent need for reform in land use practices, particularly in regions affected by strict local policies. Moreover, examining housing development through various lenses reveals how factors like construction innovation and economic viability interlink to shape current housing trends. The dynamics of increased affordability and the challenges posed by regulatory frameworks create a complex landscape that demands immediate attention. By addressing these interconnected themes, stakeholders can pave the way for a more sustainable housing environment that better serves a diverse population.
Understanding Housing Productivity and Its Challenges
Housing productivity refers to the efficiency with which homes are built and produced in relation to the resources used, such as labor and materials. Unfortunately, this sector has faced significant challenges over the decades, particularly due to land-use regulation policies that slow down construction processes. The increase in local regulations and NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) attitudes has led to smaller-scale projects that lack the economies of scale enjoyed by larger historical developments. For example, the shift from expansive subdivisions to smaller, micromanaged projects has substantially hindered housing productivity, escalating costs and limiting access to affordable housing for many Americans.
The detrimental effects of these regulations become particularly evident when examined in light of the past. During the post-war period, housing production flourished as builders were able to access larger land parcels, leading to the construction of thousands of homes at diminished costs. In contrast, today’s builders face a maze of regulatory requirements that restrict project sizes, thereby necessitating smaller firms that simply cannot compete at the same level of efficiency. As housing demand remains high, the deceleration of productivity and innovation within construction becomes a pressing concern, threatening both housing affordability and the overall economic growth of the sector.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do land-use regulations affect housing productivity?
Land-use regulations significantly inhibit housing productivity by limiting the size and scale of construction projects. This leads to the development of smaller, bespoke homes rather than mass-produced housing. Consequently, builders face increased costs and decreased efficiencies, contributing to the overall housing affordability crisis.
What is the impact of NIMBY policies on the construction industry?
NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies create barriers that restrict housing development, resulting in smaller construction firms with fewer resources for innovation. These regulations lead to higher costs and less housing supply, exacerbating the housing affordability issues faced by many Americans.
Why is housing affordability a pressing issue in relation to housing productivity?
Housing affordability has worsened due to declining housing productivity driven by stringent land-use regulations and smaller construction projects. With rising construction costs and limited supply, more Americans find homeownership increasingly unattainable, highlighting the need for reforms that promote productivity in housing development.
How do economic growth and housing productivity correlate?
Economic growth is often tied to housing productivity; when the construction industry is efficient and capable of mass production, it can contribute positively to the economy. However, restrictive land-use regulations hinder this productivity, leading to slower economic growth and exacerbating issues like housing affordability.
What role does the construction industry play in improving housing productivity?
The construction industry can improve housing productivity by embracing innovative building practices and larger-scale projects. However, land-use regulations and NIMBY sentiments must be addressed to allow builders the opportunity to produce homes more efficiently and affordably.
What are the long-term effects of decreased housing productivity on society?
Decreased housing productivity can lead to a significant intergenerational transfer of wealth, where younger generations struggle to attain homeownership. This disparity can contribute to economic inequality, social instability, and an inability for families to build wealth through property ownership.
How has the construction sector’s patenting activity changed over the years?
Since the 1970s, patenting activity in the construction sector has lagged behind other industries, indicating a decrease in innovation. This decline correlates with growing land-use regulations and the challenges faced by builders in developing larger scale housing projects.
What historical trends have influenced housing productivity in the U.S.?
Historically, housing productivity in the U.S. increased significantly from 1935 to 1970 when large-scale developments were common. Post-1970 shifts toward restrictive land-use regulations and smaller projects contributed to a decline in productivity, which has yet to recover since.
Can reforming land-use regulations enhance housing productivity?
Yes, reforming land-use regulations could enhance housing productivity by allowing for larger and more efficient construction projects. By reducing bureaucratic restrictions, builders would be incentivized to innovate and produce more affordable housing options.
What can be done to address the housing crisis related to productivity?
Addressing the housing crisis requires a multifaceted approach, including revising land-use regulations to promote larger projects, encouraging innovation in the construction industry, and fostering a pro-development culture to mitigate NIMBY sentiments.
| Key Issue | Details |
|---|---|
| Housing Affordability Crisis | High costs prevent homeownership for many Americans as prices have doubled since 1960. |
| NIMBY Land-Use Policies | Local regulations stifle construction, leading to smaller and bespoke housing projects which impact productivity. |
| Declining Productivity | Construction productivity fell by 40% from 1970-2000 despite overall economic growth. |
| Benefits of Scale | Larger firms are significantly more productive, producing four times as many units per employee as smaller firms. |
| Innovation Decline | While manufacturing innovation has increased, construction patents and R&D have lagged since 1970. |
| Impact of Historical Data | A century of census data indicates that housing productivity peaked from 1935 to 1970 before declining with increased regulations. |
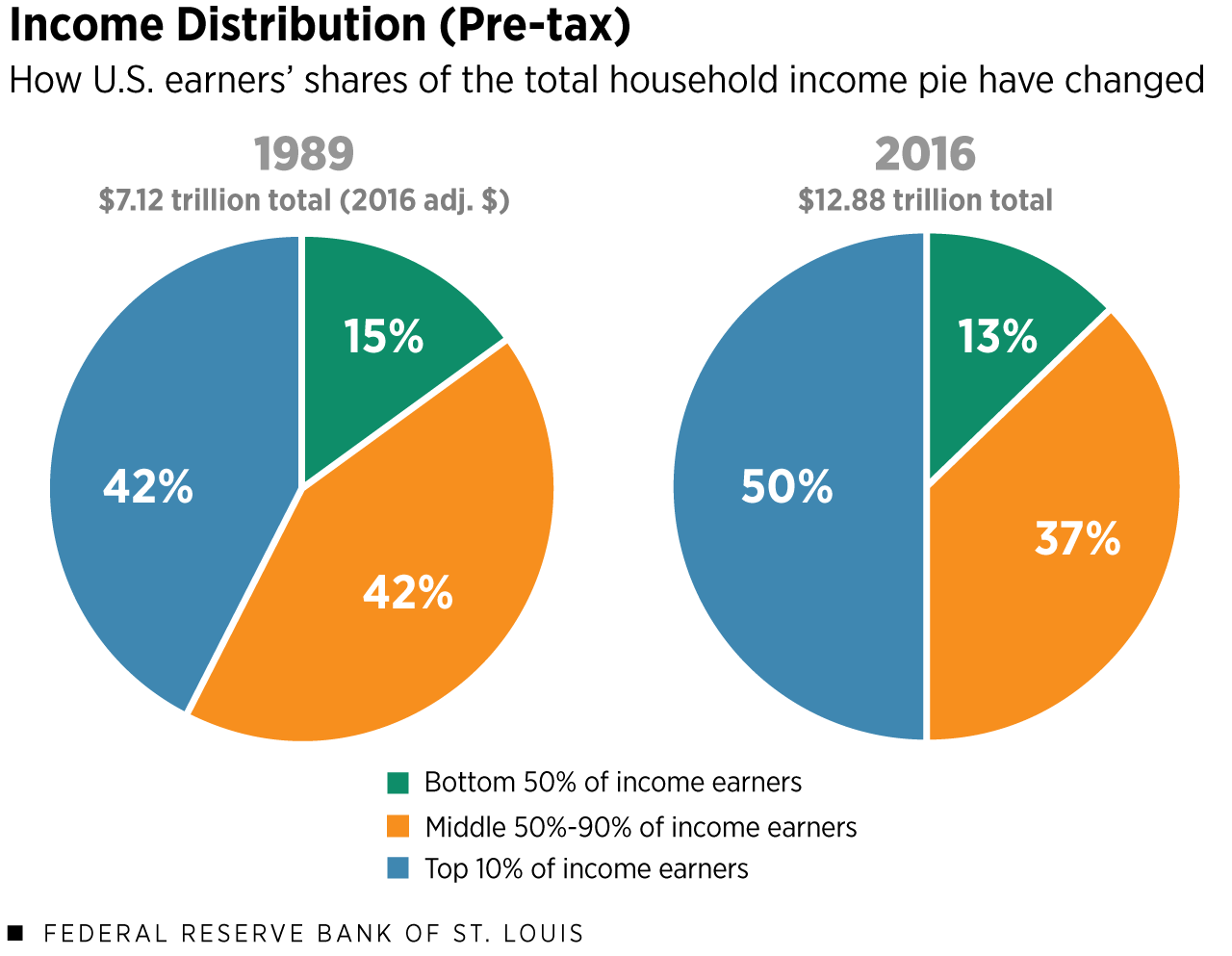
| Intergenerational Wealth Disparity | Younger demographics have significantly less housing wealth compared to older generations, exacerbating inequality. |
| Underlying Economic Models | Historical patterns indicate that regulations promote insider interests, limiting new housing developments and contributing to the crisis. |
Summary
Housing productivity remains a crucial topic in today’s economic landscape. The striking decline in construction productivity due to increasingly stringent land-use regulations has significantly impacted the ability to deliver affordable housing. With the rising costs and limited innovation in building practices, more Americans find themselves unable to attain homeownership. Efforts to reform these restrictive policies are essential to rejuvenate the housing market and improve economic outcomes for future generations.