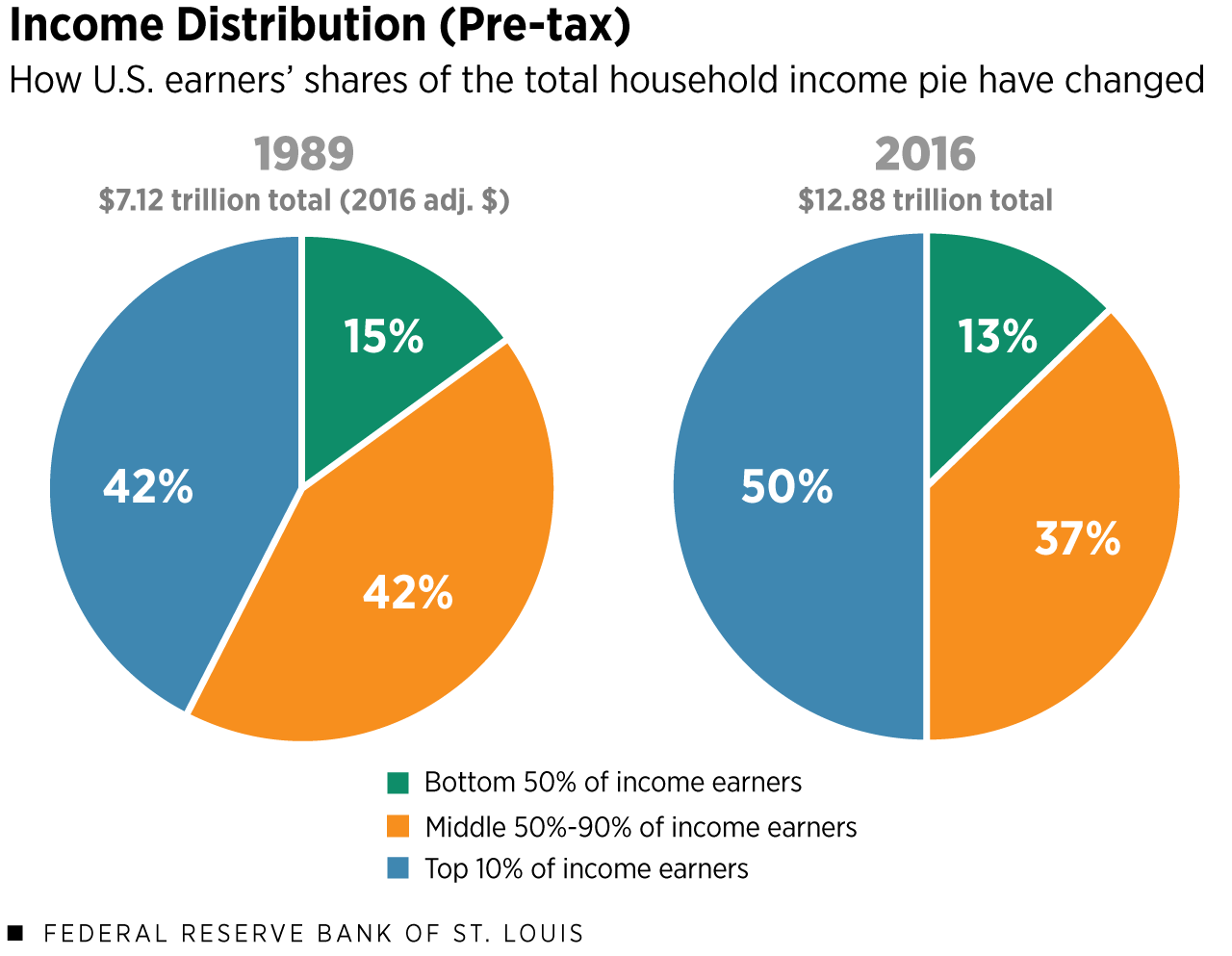
Income inequality is a pressing issue that reflects the growing divide between the rich and the poor in society. As extreme wealth continues to accumulate among billionaires, the disparities in income affect every level of economic participation, raising questions about wealth redistribution. The impact of billionaires on society is often debated, with some arguing that their philanthropy and investments in technology can drive social progress, while others highlight the harm they can cause to the environment and job markets. This dynamic creates a complex landscape where the benefits of wealth generation clash with the ethical implications of income inequality. In exploring these themes, the discourse surrounding billionaires and their role in society is more vital than ever, challenging us to reconsider how wealth is created and distributed.
The disparity in wealth distribution characterized by economic stratification underscores a critical societal concern. With a small number of individuals holding a substantial portion of resources, the consequences of financial inequity become increasingly pronounced. This phenomenon, often referred to as the wealth gap, raises significant inquiries into the moral and practical implications of extreme affluence on community welfare. As discussions about equitable resource allocation and collective prosperity emerge, the nuances of philanthropy in the face of inequality become apparent, urging a reevaluation of the systems that currently uphold such disparities. Understanding wealth disparity not only involves examining the responsibility of the affluent but also necessitates a broader dialogue about societal values and the structures that promote or hinder equitable growth.
The Complex Relationship between Extreme Wealth and Income Inequality
Extreme wealth and income inequality are often viewed as two sides of the same coin, yet their relationship is nuanced and complex. On one hand, the concentration of wealth in the hands of a few billionaires has exacerbated socio-economic disparities, leaving opportunities and resources unevenly distributed among the population. As billionaire influence grows, so does the risk of policies that favor the wealthy, leading to a further decline in equality. The top 1% not only hold a disproportionate share of wealth, but their consumption habits also have significant environmental impacts, raising questions about the sustainability of such economic structures.
On the other hand, it’s argued that wealth generation can be a mechanism for positive change. Billionaires often fund initiatives aimed at alleviating poverty and promoting sustainability through philanthropy. For instance, investments in green technology and social enterprises have the potential to create substantial benefits for marginalized communities. This dichotomy poses the question: are extreme wealth and income inequality inherently harmful, or can they coexist with a structure that fosters social good? The challenge lies in designing systems that ensure wealth is both generated and distributed in ways that prioritize public welfare.
Philanthropy: A Double-Edged Sword in Wealth Redistribution
Philanthropy has become a central theme in discussions about wealth redistribution, particularly concerning the actions of billionaires aiming to address global challenges. While substantial charitable donations from the super-rich can lead to improvements in public health, education, and environmental sustainability, they also highlight the ethical implications of private wealth influencing public welfare. Critics argue that philanthropy allows billionaires to wield power over social issues that should ideally be addressed through democratic means and government actions. The influence of wealth in the charitable sector raises questions about whose needs are prioritized, as well as the long-term sustainability of such initiatives.
Moreover, the impact of billionaires’ philanthropy often varies geographically and demographically. While urban areas may see significant investments in social programs, rural regions or communities with less visibility may be neglected. This uneven distribution of philanthropic efforts can perpetuate existing inequalities, as those in power decide what issues should be prioritized based on their values and interests. Therefore, while philanthropy can serve as a useful tool for addressing immediate needs, it is crucial to ensure that these efforts are complemented by policy measures aimed at systemic reform to achieve equitable wealth redistribution.
The Role of Corporations and Labor in Addressing Wealth Inequality
Corporations play a significant role in shaping the landscape of income inequality, as evidenced by the practices of large companies such as Walmart. While these corporations provide essential goods and services at competitive prices, they often do so at the expense of their employees, many of whom earn low wages in substandard working conditions. The strategy of maintaining low costs through wage suppression raises ethical questions about corporate responsibility and the minimal living standards that should be ensured for all workers. As panelist Shruti Rajagopalan articulated, the reliance on such corporations highlights the struggle for basic economic security among the working poor.
Encouraging fair practices such as unionization and co-determination in corporate governance could serve as a solution to this inequity. By granting workers a voice in decision-making processes, corporations may become more accountable to their employees and the communities they serve. Such reforms could create a more equitable distribution of wealth generated by businesses, challenging the status quo of extreme wealth accumulation at the top and fostering a more just economic system. Thus, the intersection of labor rights and corporate practices is critical for paving the way toward a fairer society.
Democratic Socialism: A Vision for Equitable Capitalism
The concept of democratic socialism offers a potential framework for addressing income inequality and wealth distribution in a modern economy. Advocates argue that by incorporating elements of democratic governance into the economy, we can create a system that not only allows for wealth creation but also ensures equitable access to resources and opportunities. This may involve regulating industries to protect workers’ rights, implementing policies that promote wealth redistribution, or creating public institutions that provide essential services funded by taxes on the ultra-wealthy.
Critics, however, often argue against the feasibility of such systems, claiming they may reduce incentives for innovation and investment. Yet, proponents of democratic socialism contend that a modified version of capitalism can coexist with robust social safety nets and democratic oversight. Countries like Sweden often serve as examples of how a balance can be struck between fostering economic growth while promoting social welfare. Ultimately, the challenge remains to find effective ways to implement these ideals within existing frameworks without stifling economic dynamism.
Billionaires and Society: Are They a Net Positive or Negative?
The debate over whether billionaires are a net positive or negative force in society remains polarizing. On one side, supporters argue that billionaires can drive economic growth and innovation, as their wealth enables substantial investments in various sectors, such as technology, healthcare, and renewable energy. These investments can have broader implications for job creation and advancements that benefit society at large. For instance, philanthropic initiatives aimed at combating climate change or supporting education can lead to systemic improvements for underprivileged communities.
Conversely, opponents contend that the concentration of wealth in the hands of a few undermines democratic principles and societal equity. The influence of billionaires can warp public policy to favor their interests, often at the expense of broader societal needs. This power dynamic raises questions about accountability and the true intentions behind philanthropic endeavors. Hence, the critical discourse around billionaires necessitates a thorough examination of their role and impact within the societal fabric, leading to considerations of how to balance wealth accumulation with the common good.
Environmental Impact of Extreme Wealth: A Global Concern
The environmental impact of extreme wealth is a significant concern discussed among economists and environmentalists alike. The consumption patterns associated with billionaires often contribute substantially to ecological degradation, as their lavish lifestyles can equate to higher carbon footprints. Panelist Tom Malleson noted the staggering statistic that the top 1% emit the same amount of carbon as billions of people combined. Such inequalities in environmental impact not only illustrate the stark differences in consumption but also raise ethical concerns regarding responsibility and stewardship of the planet.
Moreover, addressing these environmental issues is intertwined with the conversations surrounding income inequality and wealth redistribution. Significant investment in green technologies and sustainable practices is crucial, yet these initiatives often require capital that may not be adequately distributed within society. The challenge lies in implementing policies that facilitate a transition towards environmentally conscious practices while addressing the income disparities that hinder collective action. Achieving sustainability requires a concerted effort from both the super-rich and the broader population, emphasizing shared responsibility towards our planet.
Taxation and the Wealthy: Finding Equitable Solutions
Taxation remains a contentious issue in the discussion of wealth inequality, particularly as it relates to the ultra-wealthy. Proponents of increased taxes on billionaires often assert that these funds can be used to address critical social issues, including poverty alleviation, healthcare access, and education improvement. Striking a balance between fostering economic growth and ensuring fair contributions from the wealthy is essential for creating a more equitable society. However, it’s crucial to consider the efficacy of tax policies and their implementation to truly maximize their potential benefits for the public good.
Conversely, critics argue that excessive taxation can disincentivize investment and innovation, ultimately harming economic growth. They advocate for alternative methods of addressing income inequality that do not rely solely on taxation. Innovative strategies could involve incentivizing corporate responsibility or encouraging voluntary wealth redistribution through philanthropy. The complexity of this issue underscores the need for a multifaceted approach to taxation, where solutions are tailored to nurture both economic sustainability and social equity.
The Potential for Immigration to Impact Global Inequality
The immigration debate often intersects with discussions of global inequality, particularly regarding how allowing immigration can enhance the life conditions of those in impoverished regions. As panelist Shruti Rajagopalan highlighted, enabling people from poorer nations to seek opportunities in wealthier countries could serve as a powerful mechanism for wealth redistribution. This movement of people not only benefits individuals and families seeking better livelihoods but can also help stimulate economic growth in host countries as diverse talents and perspectives are welcomed into the workforce.
However, the conversation surrounding immigration and income inequality requires careful navigation to address the fears and concerns of the public. Societal apprehensions about job competition and cultural integration often fuel resistance to immigration policies. To facilitate a beneficial dialogue, it is important to emphasize the contributions immigrants make and to frame immigration as a collaborative solution to global inequality. By fostering empathy and understanding, societies can better harness the positive potential of immigration as a means to uplift both individuals and communities on a global scale.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary causes of income inequality in today’s economy?
Income inequality is primarily driven by factors such as extreme wealth accumulation among the top 1%, wage stagnation for low and middle-income workers, and disparities in education and access to resources. These factors contribute to the growing gap between billionaires and society, as wealth becomes concentrated in the hands of a few, limiting economic opportunities for the majority.
How does extreme wealth affect income distribution and wealth redistribution?
Extreme wealth contributes to significant income inequality by creating barriers to wealth redistribution. Billionaires often invest in initiatives that can both mitigate or exacerbate inequality, such as philanthropy aimed at addressing poverty, but their concentration of wealth can undermine democratic processes and equitable policy-making, making true wealth redistribution challenging.
What is the impact of billionaires on society and income inequality?
The impact of billionaires on society is mixed. While some billionaires engage in philanthropy that addresses income inequality and fund initiatives for social change, their substantial wealth can also lead to negative consequences. For instance, the super-rich may exert undue influence on political systems, perpetuating policies that favor their interests over those of the broader population, thereby exacerbating income inequality.
What are the arguments for and against philanthropy in relation to income inequality?
Proponents of philanthropy argue that billionaire donations can significantly address social issues and fund critical services, thereby reducing aspects of income inequality. However, critics claim that philanthropy can reinforce existing power dynamics, as wealthy individuals often control how funds are allocated, leading to paternalistic solutions rather than systemic changes needed for true wealth redistribution.
How do government policies influence wealth redistribution and income inequality?
Government policies play a crucial role in wealth redistribution and shaping income inequality. Taxation systems, social safety nets, and labor regulations determine how wealth is distributed across society. Progressive taxation, for instance, can help level the playing field, while policies favoring capital gains over labor income can exacerbate income inequality by benefiting the wealthy disproportionately.
Can income inequality be effectively addressed through reforms in corporate practices?
Corporate practices significantly influence income inequality. Implementing reforms such as fair wages, unionization, and equitable profit-sharing can help address the disparities caused by corporate practices. Advocating for a more inclusive workplace and improved labor conditions can contribute to wealth redistribution, balancing the scales of income inequality in society.
What role does education and skills development play in reducing income inequality?
Education and skills development are vital in reducing income inequality. Access to quality education equips individuals with the skills necessary to thrive in a competitive job market, ultimately improving their earning potential. By investing in education, societies can empower the disadvantaged, mitigating the effects of income inequality and promoting upward mobility.
Are there successful examples of wealth redistribution that have reduced income inequality?
Yes, there are successful examples of wealth redistribution mechanisms that have effectively reduced income inequality. Countries with robust social welfare systems, like Scandinavian nations, demonstrate how progressive taxation and comprehensive public services can lift the lowest income brackets and narrow income disparities, showing that strategic wealth redistribution can lead to a more equitable society.
How does global wealth inequality compare to domestic income inequality?
Global wealth inequality often highlights stark disparities that differ from domestic income inequality. While domestic inequality pertains to wealth distribution within a nation, global inequality illustrates how wealth concentration exists on an international scale, with billionaires from wealthier nations holding assets far exceeding the combined wealth of poorer countries, exacerbating global issues like poverty and access to resources.
What are the long-term economic implications of ignoring income inequality?
Ignoring income inequality can have detrimental long-term economic implications, including decreased social mobility, increased political instability, and weakened consumer spending. As wealth becomes increasingly concentrated, the purchasing power of poorer demographics diminishes, leading to economic stagnation and creating societal tensions that can hinder overall growth and stability.
| Key Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Extreme Wealth and Income Inequality | Debate on whether billionaires contribute positively or negatively to society, focusing on philanthropy vs. environmental harm. |
| Impact of Billionaires | Billionaires can drive job creation and support clean energy, but their carbon emissions are significantly higher than the average person’s. |
| Role of Luck in Wealth Accumulation | Wealth may be attributed to factors outside personal control, highlighting issues with meritocracy. |
| Market Economy vs. Redistribution | Arguments for maintaining a market-based economy to alleviate poverty while addressing inequalities through regulations and union support. |
| Proposed Solutions to Inequality | Ideas like property-owning democracy suggest a fairer distribution of wealth while allowing for market exchanges. |
| Global Context | Comparison of Sweden’s wealth distribution with the U.S., emphasizing the importance of a balanced market economy. |
Summary
Income inequality remains a pressing issue in society as it influences economic stability and social cohesion. The debate surrounding the benefits versus the drawbacks of extreme wealth highlights the complex dynamics at play, including the role of billionaires in philanthropy and environmental impacts. Solutions to mitigate income inequality must balance the imperative for a vibrant market economy with effective regulations to ensure fair wealth distribution. Understanding these nuances is crucial for addressing the challenges presented by income inequality.