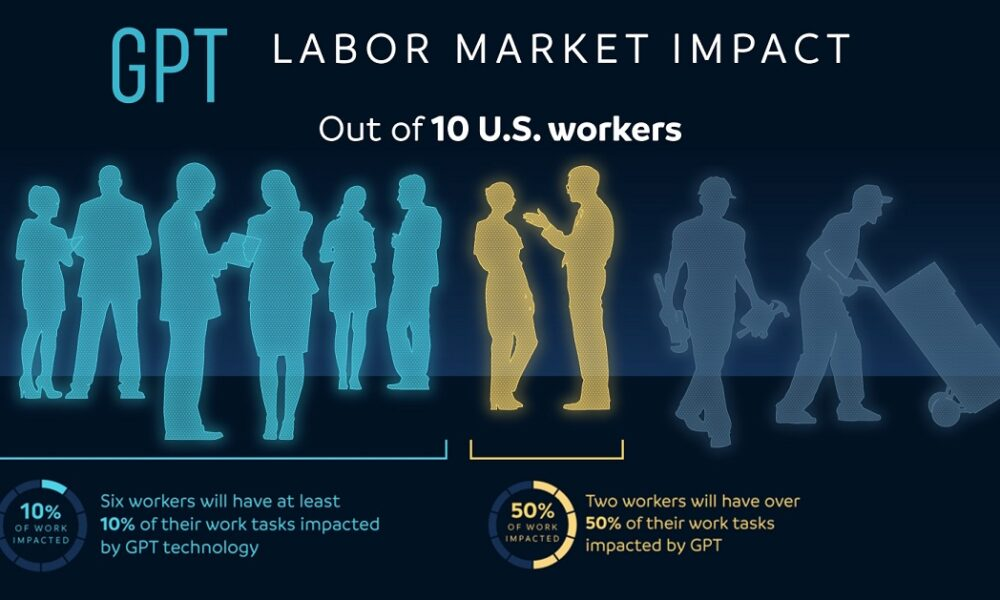
The impact of AI on the labor market is increasingly evident as researchers delve into how artificial intelligence is reshaping the workforce. A recent study highlights significant shifts driven by technological disruption, particularly in relation to traditional job roles. Analysts are observing an intriguing trend toward the emergence of specialized STEM job growth, which offers promising opportunities while simultaneously raising concerns over occupational churn. As automation continues to evolve, the dialogue around harmonizing technology and employment becomes crucial, ensuring that the benefits of AI are balanced against the potential for job displacement. In this rapidly changing landscape, understanding AI’s influence on the labor market is more important than ever for workers and employers alike.
The effects of artificial intelligence on employment dynamics have sparked widespread discourse, with many experts contemplating the future of work in the age of machines. Studies exploring the relationship between automation and job security reveal a complex tapestry of advancing technology, where some sectors thrive while others face decline. As we analyze workforce transformations driven by innovative technologies, the term “technological disruption jobs” becomes increasingly relevant, shedding light on the nuances of this evolution. Furthermore, the emphasis on STEM competencies highlights the pressing need for educational reforms that align with emerging industry demands. Consequently, the ongoing conversation around AI and its implications for labor creates a pressing need for strategies that respect and leverage human potential in conjunction with technological advancements.
The Historical Impact of Technological Disruption on Jobs
Throughout the last century, the U.S. labor market has witnessed numerous technological disruptions that have significantly altered the landscape of employment. Economists David Deming and Lawrence H. Summers, in their recent study, examined over a hundred years of occupational churn to provide insights into how historical technological advancements have been integrated into the workforce. The paper highlighted periods of stability and transformation, revealing that, contrary to popular belief, technological innovations don’t always lead to job losses but can coexist with job growth in various sectors.
By analyzing a century’s worth of U.S. Census data, the researchers discovered patterns of technological influence on jobs that experienced both volatility and stability. Notably, during the late 20th century, the economy appeared resilient to disruptions caused by advancements such as computing technologies. However, as the 21st century unfolded, the introduction of AI and automation hinted at a more complex interplay between technology and the workforce, suggesting that while certain jobs may disappear, new opportunities often emerge.
AI’s Role in Shaping the Future Workforce
The introduction of artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly seen as a pivotal factor in reshaping the future labor market. As highlighted in the findings of Deming and Summers, AI is not merely a new technology but potentially a transformative force that is comparable to the advent of electricity or the computer. By generating job polarization, AI trends indicate a shift towards high-skill, high-wage positions, which leads to concerns about the sustainability of lower-wage jobs across various sectors.
Furthermore, the research indicates a steady rise in STEM job growth, underscoring the increasing demand for technical skills in the workforce. AI-related roles such as data analysts and software developers have surged, with their share of the employment market rising significantly. This trend reflects the need for upskilling and retraining within the contemporary labor force, as workers must adapt to the educational demands posed by AI and advanced technologies.
Understanding Occupational Churn in a Tech-Savvy Economy
Occupational churn refers to the continuous influx and outflux of jobs as industries evolve. The recent study conducted by Harvard economists reveals that understanding this phenomenon is crucial in dissecting the effects of technological disruptions on employment. Historically, periods of low employment churn have indicated economic stability; however, recent data suggests a shift as AI technologies are introduced. This has created volatility in certain job sectors while simultaneously expanding opportunities in others, particularly those requiring advanced skills.
The analysis of occupational churn highlights that while some sectors are experiencing declines, particularly low-paid service jobs, others are witnessing robust growth. By understanding the causes behind these shifts, policymakers and educators can better prepare current and future workers for the rapidly evolving labor landscape that is increasingly influenced by automation and artificial intelligence.
The Rise of STEM Jobs Amidst Automation
One prominent finding from the research was the remarkable increase in jobs associated with science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). As industries continue to adapt in the face of automation, the share of STEM jobs has surged considerably, jumping from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024. This almost 50% increase is a clear indication that as traditional jobs erode due to technological disruption, a demand for skilled professionals in technology-related fields is on the rise.
The parallel growth of STEM roles coincides with companies increasingly investing in frontier technologies such as AI. As firms recognize the importance of technical expertise in driving innovation, they are not only creating new job openings in these fields but also reshaping career pathways to ensure these skills are cultivated in the workforce. Consequently, individuals entering the job market or considering career changes may find substantial opportunities in STEM-related domains.
Navigating Workforce Changes Amid Automation Anxiety
The term “automation anxiety” has been prevalent in discussions about the future of work, especially regarding predictions that suggest a large portion of jobs might be at risk of being displaced. The nuanced findings from the Harvard study suggest that while anxiety about automation is valid, the actual effects have been more complex. Between 2010 and 2017, the pace of job disruption seemed to stabilize, providing a buffer against fears of widespread unemployment due to evolving technologies.
However, as revealed in the data analysis, the trends have shifted notably since 2019, implying that automation may create new job opportunities even while specific roles may decline. Emphasizing a balanced understanding of these dynamics will be essential for workers, companies, and policymakers as they navigate the waves of change driven by AI and other advanced technologies.
The Impact of AI on Employment Distribution
AI’s integration into the workforce is causing shifts in job distribution, particularly in sectors historically dominated by lower-paid service jobs. Evidence from the Harvard study indicates that while employment in low-paid positions has generally stagnated or declined, new opportunities in high-skilled jobs are emerging. The clear implication is that investment in AI is reshaping the overall structure of employment, favoring roles that require advanced technical expertise and diminishing the viability of traditional, low-skilled labor.
In the context of e-commerce and retail, AI-driven operational efficiencies have dramatically changed the job landscape, contributing to a significant drop in retail sales jobs. These shifts are a reminder of how quickly technology can disrupt industries overnight, highlighting the need for ongoing adjustment and adaptation within the workforce as companies evolve to meet consumer demands and operational efficiencies.
The Role of Knowledge Workers in an AI-Driven Economy
With the continuing evolution of AI, knowledge workers are facing both opportunities and challenges. As highlighted by Deming, companies are increasingly expecting more from employees, particularly in knowledge-intensive roles such as finance, management, and journalism. As AI technologies enhance productivity, employers may demand quicker turnaround rates, creating pressure on workers to adapt swiftly to technological advancements, lest they find themselves at risk of obsolescence.
The implications for knowledge workers in AI-driven environments are profound. While AI can act as a powerful tool that augments human capabilities, it may also threaten the traditional employment structures within various industries. Striking a careful balance between harnessing AI’s potential and preserving meaningful employment opportunities will require not only proactive workforce development strategies but also an openness to reevaluating the nature of work itself.
Preparing the Workforce for Technological Change
In light of the findings regarding occupational churn and AI’s impact on job structures, preparing the workforce for ongoing technological change is more critical than ever. Educational systems and vocational training must align more closely with the evolving demands of the labor market, particularly in fostering skills that are complementary to AI technologies. This includes encouraging interest in STEM fields and promoting lifelong learning as industries evolve.
Employers also play a vital role in preparing their workforce for the future. By investing in employee training and development programs that emphasize adaptability and technological proficiency, companies not only bolster their competitiveness but also support the broader economic environment. Collaboration between educational institutions, businesses, and government bodies will be essential in creating a workforce ready to negotiate the challenges and opportunities posed by rapid advancements in technology.
Harnessing the Power of AI While Preserving Human Employment
As businesses forge ahead with the adoption of AI and other advanced technologies, striking a balance between harnessing these benefits and preserving meaningful human employment is crucial. Acknowledging the potential of AI to enhance productivity and effectiveness should not overshadow the importance of maintaining a diverse and inclusive labor market. Strategies that prioritize workforce retraining and professional development will be essential to ensure that displaced workers can transition into new roles that AI may create.
Additionally, fostering a dialogue around technological ethics is imperative. Discussions regarding the responsible use of AI can help shape policies that promote positive employment outcomes while mitigating any adverse effects of automation. Engaging stakeholders across various sectors will ensure that the impact of technological change is managed thoughtfully, benefiting both businesses and workers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the AI impact on the labor market in the U.S.?
The AI impact on the labor market is significant, with evidence indicating a shift in occupational churn since 2019. Recent research shows that AI is reshaping job distributions, leading to increased demand for high-skilled positions, particularly in STEM fields, while lower-paid service roles are decreasing.
How is artificial intelligence affecting workforce dynamics and job opportunities?
Artificial intelligence is transforming workforce dynamics by causing job polarization to end and fostering growth in high-compensation roles that require advanced skills. Additionally, investments in AI are contributing to unprecedented expansions in STEM job opportunities, as companies seek technical talent to leverage new technologies.
What is occupational churn analysis and how does it relate to AI in the labor market?
Occupational churn analysis measures changes in job distributions across industries over time. Recent findings reveal that AI contributes to increased churn, indicating that job markets are evolving faster, with substantial declines in low-paid jobs juxtaposed against growth in high-skilled positions.
What trends have emerged regarding STEM job growth due to AI technologies?
The trend toward STEM job growth is notable, with the share of these positions increasing from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024. This expansion reflects the rising demand for technology-related skills as AI integrates into various sectors, driving companies to invest more in technical roles.
How do researchers believe we can harmonize technology and employment amidst AI disruptions?
Researchers suggest harmonizing technology and employment involves adapting education and training systems to prepare workers for AI-driven job requirements, promoting skills relevant to emerging technologies, and ensuring that labor policies support workforce transitions while minimizing job displacement.
What evidence suggests AI is responsible for job loss in retail and service sectors?
Evidence shows that between 2013 and 2023, retail sales jobs dropped significantly due to AI and e-commerce adoption, which rapidly transformed retail operations and customer behaviors. This shift, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, indicates that many low-paid service jobs may not return to pre-pandemic levels.
How has technological disruption impacted the demand for various job roles over the last century?
Technological disruption, including the rise of AI, has impacted demand for job roles by enabling significant structural changes in employment trends. Research indicates a decline in middle-income jobs while high-paying, skilled roles have surged, highlighting the necessity for workers to adapt to evolving industry needs.
In what ways is AI expected to change the expectations of knowledge workers in the future?
With the advent of AI, knowledge workers can expect increased demands for productivity and efficiency. As companies harness AI’s capabilities, expectations on turnaround times for tasks will likely shorten, compelling workers to meet accelerated output requirements.
What can we anticipate regarding the future of artificial intelligence and its influence on job stability?
While AI is expected to continue transforming job markets, the future points toward both opportunities and challenges. Certain roles may face displacement due to automation, but new job avenues in tech and high-skilled sectors will likely emerge, prompting a need for continuous learning and adaptation.
| Key Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Job Polarization End | Shift towards high-skilled, high-paid jobs instead of growth in low-paid positions. |
| Rise in STEM Jobs | STEM jobs increased from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024, a 50% rise. |
| Decline in Low-paid Service Work | Flat or declining in low-paid service roles since 2019, potentially due to AI. |
| Retail Job Reduction | Retail sales jobs decreased from 7.5% to 5.7% from 2013 to 2023 due to automation and e-commerce. |
Summary
The AI impact on the labor market is becoming increasingly evident as studies show significant shifts in employment dynamics due to technological innovations. Recent research highlights the transformation of job profiles, moving towards high-skilled occupations while witnessing a reduction in low-paid jobs, particularly in sectors like retail and services. This suggests that AI not only changes the types of jobs available but also emphasizes the need for workers to adapt to these advancements to remain competitive in the evolving job landscape.