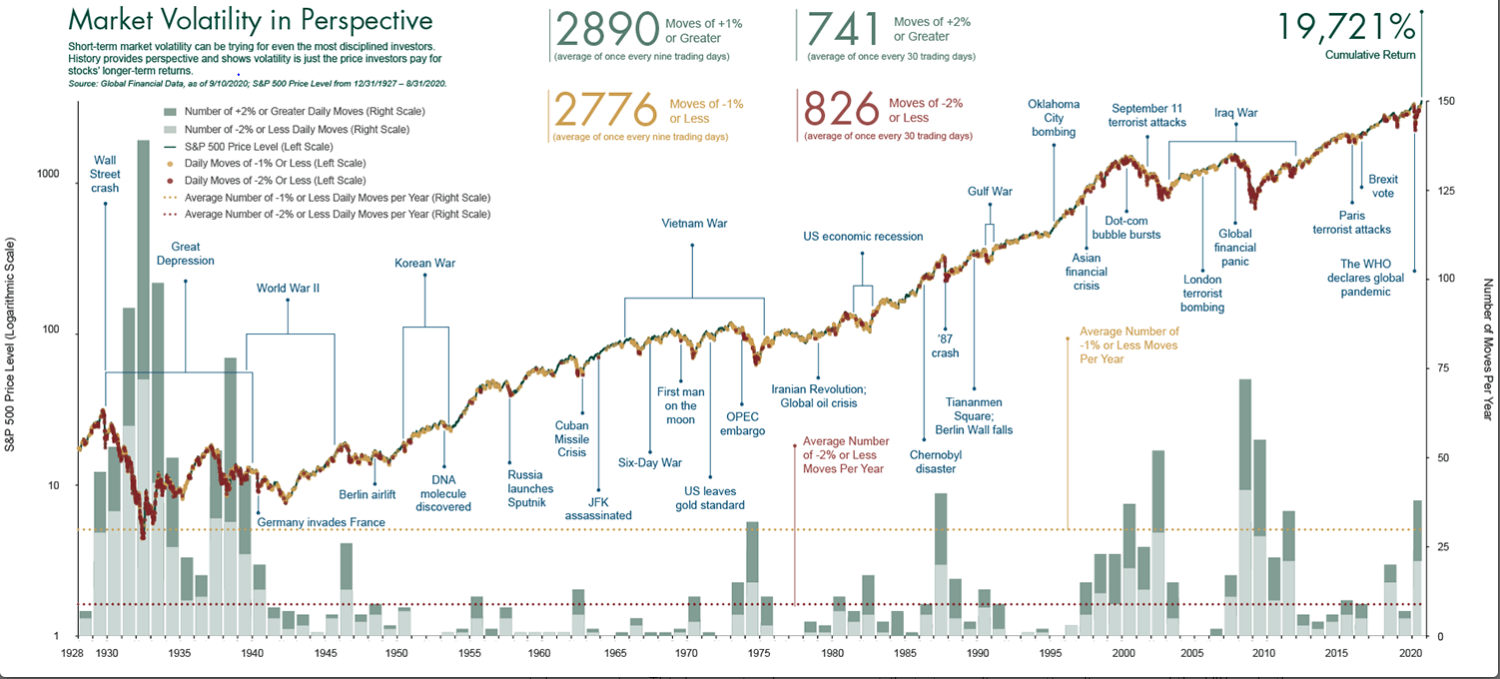
The U.S. economy recession is looming on the horizon as multiple factors converge to threaten financial stability. Recent turmoil in U.S. markets, exacerbated by escalating trade wars with major trading partners like China, Mexico, and Canada, has left investors jittery and uncertain about the economic future. With the University of Michigan’s consumer sentiment index plummeting to its lowest levels since late 2022, concerns about consumer confidence are palpable. Moreover, the Federal Reserve faces a tricky dilemma regarding interest rates as it weighs the potential need for cuts amidst rising fears of a prolonged downturn. As these economic indicators unfold, it becomes increasingly crucial to assess their implications for both everyday Americans and the broader market landscape.
As the nation navigates turbulent economic waters, the potential for a downturn in the U.S. economy grows stronger. Factors such as the destabilizing trade conflict and shifts in consumer confidence highlight critical vulnerabilities within American markets. With rising tensions influencing financial landscapes, analysts and economists are closely watching the Federal Reserve’s next moves on interest rates. The sentiment among consumers is shifting, signaling deeper concerns about the economic outlook. These developments point to a more significant issue at stake, raising questions about monetary policy and its ability to steer the economy away from the risk of recession.
Assessing the U.S. Economy’s Current State
As of early 2025, the U.S. economy finds itself at a critical juncture, where significant shifts in policy and external circumstances are creating a complex economic landscape. The recent heavy losses in U.S. markets, driven by reactionary tariffs levied by countries like China, Mexico, and Canada, have raised alarms among economists and investors alike. These changes do not occur in a vacuum, as they intertwine with consumer sentiment, which has shown signs of deterioration, reflected in the University of Michigan’s consumer sentiment index. Understanding these shifts is vital, as they could herald an impending recession, prompting urgent discussions on the future trajectory of the American economy.
Furthermore, the interplay between government policy and market response is becoming increasingly critical. Analysts are scrutinizing whether the current administration’s tariff strategy will provide any long-term economic benefits or merely exacerbate risk perceptions among consumers and investors. The erratic nature of these policies has led many to adopt a cautious approach, impacting consumer spending and willingness to invest. The looming threat of recession, driven by such uncertainties, poses significant challenges, making it imperative to track economic indicators closely.
Impact of the Trade War on U.S. Markets
The ongoing trade war has far-reaching consequences for U.S. markets, with investor confidence teetering on the edge. As tariffs are imposed, the immediate effects include volatile stock prices and heightened risks for businesses that depend on imports and exports. This turmoil underscores the interconnectedness of global trade systems, where changes in policy not only affect domestic markets but also reverberate across international borders. Investors are fearing a prolonged trade conflict, which could trigger a broader economic downturn, leading to a vicious cycle of reduced spending and investment.
Additionally, the trade war contributes to growing uncertainty among businesses and consumers alike. As economic indicators, including consumer sentiment and hiring rates, signal a cooling market, companies are re-evaluating their strategies and investment plans. This ‘wait and see’ mentality hampers economic growth, further exacerbating fears of a recession. In light of these dynamics, it is essential to analyze how ongoing tensions will shape the U.S. markets and economy, necessitating a proactive approach to mitigate risks and adapt to an evolving landscape.
Federal Reserve’s Dilemma: Interest Rates and Inflation
The Federal Reserve is currently grappling with a complex mission: balancing the dual objectives of stimulating economic growth while controlling inflation—an increasingly challenging task amidst the backdrop of escalating tariffs and market instability. With pressure mounting to cut interest rates to support lagging economic indicators, the specter of inflation looms large, forcing policymakers into a precarious tightrope walk. High-interest rates could stifle consumer spending and further dampen economic activity, yet undermining them may lead to runaway inflation, complicating recovery efforts.
Moreover, the Federal Reserve’s decisions hold immense weight in shaping future economic conditions. As the consumer sentiment index reflects declining confidence and hiring slows, the Fed must consider how its monetary policy will impact employment and income levels. The trade-offs between cutting rates and maintaining price stability are at the forefront of economic discussions, as they may very well determine the trajectory of the U.S. economy in the coming months. Thus, the Fed’s approach will be closely monitored as a bellwether for broader economic health.
Consumer Sentiment and Economic Confidence
The University of Michigan’s consumer sentiment index serves as a crucial barometer for gauging public confidence in the U.S. economy. The recent drop to its lowest point since late 2022 is a troubling sign, reflecting growing concerns over economic stability amid trade tensions and rising interest rates. Consumer sentiment is critical as it influences spending habits, which in turn directly impacts economic growth. When confidence wanes, consumers are less likely to make significant purchases or investments, creating a ripple effect throughout the economy.
In addition, understanding consumer sentiment is essential for predicting possible recessionary trends. If consumers feel uncertain about their financial outlook, they may adjust their spending behaviors, which directly affects businesses’ revenue streams. Consequently, evaluating and addressing the factors contributing to declining sentiment—such as job stability and market performance—becomes imperative for policymakers to foster an environment conducive to sustained economic growth. Enhancing consumer confidence is a fundamental step towards mitigating recession risks and promoting overall economic resilience.
The State of U.S. Hiring and Employment
Hiring trends in the United States have recently shown signs of cooling, raising further concerns about the potential onset of a recession. Economic indicators suggest that businesses are hesitant to expand their workforce, partly due to uncertainties surrounding the trade war and government policy. When organizations adopt a cautious stance on hiring, it can lead to stagnation in economic growth, contributing to higher unemployment rates and diminished consumer spending, ultimately creating a self-reinforcing cycle of economic decline.
Furthermore, the implications of slowed hiring reach far beyond mere employment numbers; they affect wage growth and consumer purchasing power. When companies are reluctant to hire or offer promotions, it can stifle income growth, which is critical for maintaining consumer confidence. This, in turn, leads to decreased spending, exerting additional pressure on the economy. Thus, addressing the issues impacting hiring is not only vital for job seekers but also for restoring momentum in the broader economic landscape.
Understanding Recession Risks in Today’s Economic Climate
The possibility of a recession looms larger amid the current economic climate, fueled by escalating trade tensions and volatile markets. Economists express growing concern that the accumulation of adverse factors—including the trade war, stock market fluctuations, and shifting government policies—could precipitate a recession within the upcoming year. The interconnectedness of these components highlights the fragility of the current economic situation, necessitating a keen awareness of risk factors that may spark economic downturns.
Moreover, discerning the nuances between recession and stagnation is vital for policymakers and businesses alike. Historical patterns suggest that economies facing both inflationary pressures and stagnant growth may lean towards a stagflation scenario reminiscent of the 1970s, where rising costs coincide with diminishing economic activity. Understanding these risks enables stakeholders to implement proactive measures, fostering resilience within the economy and preparing for potential challenges that lie ahead.
The Importance of Government Spending Cuts
The dialogue surrounding government spending cuts has intensified as fiscal pressures mount in tandem with economic uncertainty. Some policymakers advocate that reducing budget deficits could stabilize the economy, especially given the growing national debt. However, the potential short-term repercussions of these cuts could further exacerbate economic slowdowns, as decreased government spending often translates into less overall economic activity and employment. Balancing fiscal responsibility with the need for immediate economic support presents a challenging dilemma that requires careful navigation.
Additionally, the impact of government spending cuts can be particularly pronounced in essential sectors, including healthcare and education. As these cuts may disproportionately affect lower-income populations and vital services, they can lead to heightened social inequalities and increased public discontent. Recognizing the potential ramifications of spending cuts highlights the complexity of achieving economic stability while ensuring equitable growth for all Americans—an endeavor that must remain at the forefront of economic discussions.
Investor Sentiment Amidst Economic Uncertainty
Investor sentiment plays a pivotal role in shaping market trajectories, especially during turbulent times. The current climate, influenced heavily by trade wars and erratic government policies, has led to heightened anxiety among investors. Many are adopting a defensive posture, preferring to wait out the volatility rather than risking investments in an unpredictable environment. This shift in sentiment can dramatically impact stock prices and overall market stability, often resulting in sharp sell-offs in the face of bad news, further intensifying market fluctuations.
Furthermore, restoring investor confidence is crucial for fostering a stable economic outlook. As uncertainties surrounding tariffs and interest rate policies persist, gaining clarity on government actions and their implications will be pivotal. Transparent and consistent communication from policymakers could help alleviate fears and encourage reinvestment. Ultimately, bolstering investor confidence contributes to economic recovery efforts, as sustained investment is necessary for driving growth and stability in the U.S. markets.
Navigating the Future of U.S. Economic Policy
The trajectory of U.S. economic policy remains uncertain, shaped by the ongoing trade war and challenges faced by the Federal Reserve in managing interest rates. Policymakers must navigate a delicate balance between stimulating growth and containing inflation, all while responding to external pressures and domestic demands. The political landscape adds further complexity, with differing views on tariffs and their impact on the economy complicating consensus on effective measures moving forward.
As stakeholders look to the future, it is crucial to implement data-driven policies that promote sustainable growth while addressing the needs of American consumers and businesses. Engaging in dialogue with economists, businesses, and community leaders can provide valuable insights into the challenges faced and potential pathways for growth. In doing so, a comprehensive economic strategy can be developed, focusing not only on immediate recovery but also on ensuring long-term stability in the face of an evolving global landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is the trade war affecting the U.S. economy and recession risks?
The ongoing trade war, particularly with major partners like China and Mexico, is creating substantial uncertainty in the U.S. economy. Tariffs imposed in retaliation to U.S. tariffs on imports have led to higher costs for American businesses and consumers. This trade friction is contributing to a decline in consumer sentiment and could increase the risk of a recession as consumers scale back spending.
What role does the Federal Reserve play in mitigating recession risks in the U.S. economy?
The Federal Reserve can influence the U.S. economy during a recession by adjusting interest rates. Lowering rates can stimulate growth by making borrowing cheaper, encouraging both consumer spending and business investment. Given current economic challenges, including trade conflicts and waning consumer confidence, the Fed will need to carefully consider its approach to interest rates to avoid exacerbating the recession risk.
How might the consumer sentiment index indicate potential recession in the U.S. economy?
The consumer sentiment index provides insights into how individuals feel about the economy’s current and future state. A drop in this index, as observed recently, typically signals decreased consumer confidence, which can lead to reduced spending and investment, ultimately increasing the risk of a recession in the U.S. economy.
Are U.S. stock market fluctuations a sign of impending recession?
Significant fluctuations or declines in the U.S. stock market can be indicative of underlying economic issues, including fears of a recession. A crashing stock market often reflects investor concerns about economic stability and can further undermine consumer confidence, potentially leading to a cycle that exacerbates recession risks.
What impact do interest rates have on the potential for a U.S. economy recession?
Interest rates are a critical factor in the overall health of the U.S. economy. When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, it can slow down borrowing and spending, which may contribute to a recession. Conversely, lowering rates can spur economic activity. The balance maintained by the Fed regarding interest rates is crucial in preventing a recession during turbulent economic periods.
How does government spending influence the risk of recession in the U.S. economy?
Government spending plays a significant role in economic activity. If spending is cut substantially, it can lead to reduced economic output and consumer spending, heightening the risk of a recession. Such fiscal policy changes in response to political pressures can create instability and exacerbate fears of economic downturn.
What is the potential impact of a U.S. fiscal crisis on recession risk?
A U.S. fiscal crisis, such as a government shutdown or failure to raise the debt ceiling, can create severe implications for the economy. It can disrupt government services, lower consumer confidence, and chill investment. These factors could increase the likelihood of a recession as uncertainty drives businesses and consumers to be more cautious.
Why is increasing perceptions of risk important in understanding U.S. economic recession?
Increased perceptions of risk can influence investor behavior and consumer confidence negatively. This sense of unpredictability can lead to reduced spending and investment, which are vital for economic growth. Therefore, rising risk perception can be a major contributor to triggering a recession within the U.S. economy.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Heavy Market Losses | U.S. markets experienced significant declines after tariffs were imposed by China, Mexico, and Canada in response to U.S. tariffs. |
| Consumer Sentiment Decline | The University of Michigan’s consumer sentiment index dropped to its lowest level since November 2022, indicating waning consumer confidence. |
| Economic Predictions | Economist Jeffrey Frankel warns of a potential recession within a year due to several factors including a trade war and stock market crashes. |
| Impact of Tariffs | Frankel argues that tariffs hurt investment and reduce market confidence, contrary to claims that they support growth. |
| Federal Reserve’s Dilemma | The Fed faces a challenge in deciding whether to cut interest rates to support the economy or keep them stable to control inflation. |
Summary
The U.S. economy recession is a pressing concern as various economic indicators point to deteriorating conditions. With market volatility exacerbated by tariff disputes and plummeting consumer sentiment, fears of a recession loom larger. Economists like Jeffrey Frankel highlight the complex interplay of factors leading to increased risk and instability in the economy. The Federal Reserve is caught in a critical position, weighing its options to stimulate growth against the need to maintain inflation controls, further complicating the economic landscape as the potential for recession grows.